Introduction
Because of Svelte’s popularity over the years, many companies are beginning to migrate their applications or build new ones using the framework. However, developers have had difficulty implementing features such as routing in their web applications while using Svelte.
Sveltekit includes the features that Svelte lacks, saving developers time and allowing us to create complex hybrid web applications with relative ease.
Steps we’ll cover:
- What is Sveltekit
- Create Sveltekit Application
- Create the App UI
- Read Blogs
- Create New Blog
- Update Blog
- Delete Blog
What is Sveltekit
SvelteKit is a framework for creating web applications of all sizes, with a beautiful development experience and flexible filesystem-based routing. It compiles your components into a vanilla JavaScript that is highly optimized.
Sveltekit helps you build web apps that are fiendishly complicated with all of the modern best practices, such as build optimizations, offline support, prefetching pages before the user initiates navigation, and generating configurable HTML pages on the server or in the browser at runtime or build-time with minimal code.
It uses Vite in combination with a Svelte plugin to deliver a lightning-fast and feature-rich development experience with Hot Module Replacement (HMR), in which changes to your code are instantly reflected in the browser.
Prerequisites
To get the best out of this tutorial, prior knowledge of Svelte is required, and ensure you have Node.JS version 16 or later installed. The code for this tutorial is available on Github
Create Sveltekit Application
With the above requirements met, let's create a new Sveltekit application by running the following commands.
npm create svelte@latest crud-app
The above command will prompt you to select the configurations for your project. Your selection should look like the one in the screenshot below.
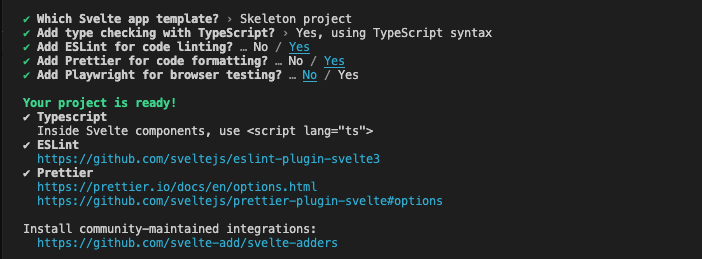
Now change the directory into the project folder and install the required dependencies with the command below.
cd crud-app
npm install
The above command will install all the required dependencies to run this application.
Create the App UI
Now let's create the UI for this application using Sveltematerialui. This UI framework provides us with all the components we need to create our UI. It was developed to allow you to install the component you want, keeping your application as minimal as possible.
To get started, run the command below to install the components we need.
npm i -D @smui/button @smui/data-table @smui/dialog @smui/textfield @smui/linear-progress @smui/card
The above comand will install the the button, textfield, and data-table components.
Next, add the Sveltematerial UI CDN to the app.html file to use the default theme.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/svelte-material-ui@6.0.0/bare.min.css" />
Then create a components folder in the src folder and create a Table.svelte file to add a data table to display the posts we'll get from the Refine-fake-API.
<DataTable table$aria-label="User list" style="width: 100%;">
<Head>
<Row>
<Cell numeric>ID</Cell>
<Cell>Title</Cell>
<Cell>Image</Cell>
<Cell>Date Created</Cell>
<Cell>Actions</Cell>
</Row>
</Head>
<Body>
{#each items as item (item.id)}
<Row>
<Cell numeric>{item.id}</Cell>
<Cell>{item.title}</Cell>
<Cell><img width="100" src={item.image?.[0]?.url} alt="" /></Cell>
<Cell>{item.createdAt}</Cell>
<Cell>
<a href={`/post/${item.id}`}>Edit</a>
<Button>Delete</Button>
</Cell>
</Row>
{/each}
</Body>
<LinearProgress
indeterminate
bind:closed={loaded}
aria-label="Data is being loaded..."
slot="progress"
/>
</DataTable>
In the above code snippet, we have DataTable that will display the data from Refine-fake-API. Each of the data we'll display on the table cell will have a corresponding edit and delete button to modify the details of the data.
Then import the components and declare the necessary variables.
<script lang="ts">
import DataTable, { Head, Body, Row, Cell } from '@smui/data-table';
import LinearProgress from '@smui/linear-progress';
import Button from '@smui/button';
export let items: any[] = []
export let loaded = false
</script>
In the above code snippet, we imported the SMUI components we need, and we declared the items and loaded variables, which will be passed as props to this component.
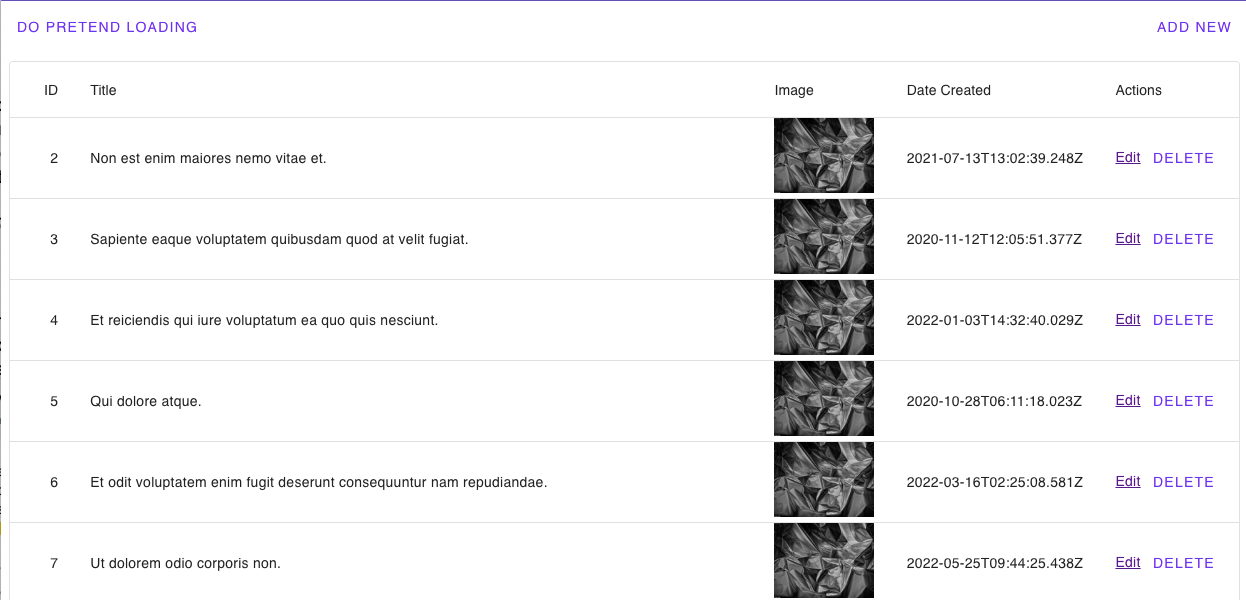
Read Blogs
Now in the +page.svelte routes, add the code snippets below to read posts from the Refine-fake-API using the Javascript fetch API, and so they are displayed on our data table.
<script lang="ts">
import { onMount } from 'svelte';
import Table from "../components/Table.svelte"
type Post = {
createdAt: Date;
image: any;
content: string;
title: string;
id: number;
};
let items: Post[] = [];
let loaded = false;
onMount(() => loadThings(false))
function loadThings(wait: boolean) {
if (typeof fetch !== 'undefined') {
loaded = false;
fetch('https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev/posts')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) =>
setTimeout(
() => {
items = json;
loaded = true;
},
// Simulate a long load time.
wait ? 2000 : 0
)
);
}
}
</script>
<Table items={items} loaded={loaded}/>
In the above code snippet, we created a Post type to tell Typescript the objects we'll be accessing from the post data.
Then we created the items variable to be a placeholder for the posts and created a loadThings function to fetch data from the API and update the items variable. The loadThings function will be called when the components mount, which are implemented in Svelte using the onMount decorator.
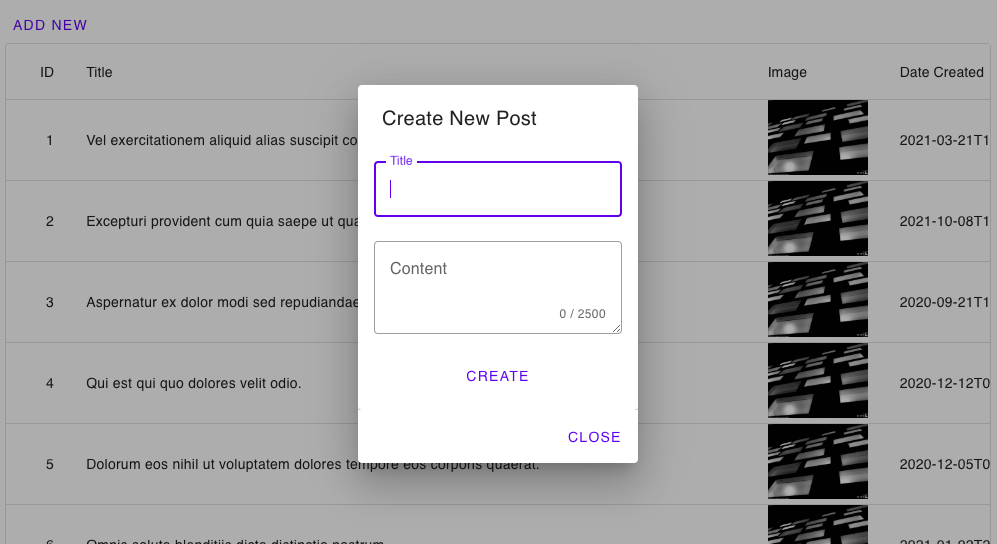
Create New Blog
With the read blog features out of the way, let's add a UI to allow the users to create new blog posts. To do that, create a Dialog.svelte file in the components folder and add the code snippet below.
<script lang="ts">
// @ts-nocheck
import Dialog, { Title, Content, Actions } from '@smui/dialog';
import Textfield from '@smui/textfield';
import HelperText from '@smui/textfield/helper-text';
import CharacterCounter from '@smui/textfield/character-counter';
import Card from '@smui/card';
import Button from '@smui/button';
let title = '';
let content = '';
export let open = false;
</script>
<Dialog bind:open selection aria-labelledby="list-title" aria-describedby="list-content">
<Title id="list-title">Create New Post</Title>
<Content id="mandatory-content">
<Card padded>
<Textfield variant="outlined" bind:value={title} label="Title">
<HelperText slot="Title">Helper Text</HelperText>
</Textfield>
<br />
<Textfield textarea input$maxlength={2500} bind:value={content} label="Content">
<CharacterCounter slot="internalCounter">0 / 100</CharacterCounter>
</Textfield>
<br />
<Button on:click={createPost}>Create</Button>
</Card>
</Content>
<Actions>
<Button action="accept">Close</Button>
</Actions>
</Dialog>
In the above code snippet, we used the Dialog component to hide and show a modal, the Card to group the Textfield together, and a Button component to submit the data.
In the button, we created four variables, open to store the initial state of the modal which will be passed as props from the root route, title and content to store the value of the input fields by binding them to the respective inputs.
Then we attached an event handler that calls the createPost function, which will be created later to send a request to the Refine-fake-API.
Now add the code snippets below in the script tag to create createPost function.
async function createPost() {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev/posts`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
title,
content,
createdAt: Date.now()
})
}).then((res) => {
res.json();
open = false;
});
}
In the above snippet, Then we send a POST request to the createPost function and pass in our JSON data in the request body.
The Refine-fake-API takes more data than we specified in the payload, we only send the data we want to display to the user.
Lastly, add the code snippet below to the +page.svelte file to add a button that will show the modal.
<script>
...
import Button from '@smui/button';
import Dialog from '../components/Dialog.svelte';
...
</script>
let open = false;
<div style="display:flex; justify-content:space-between">
<Button on:click={() => (open = true)}>Add New</Button>
</div>
<Table {items} {loaded} />
<Dialog {open} />
In the above code snippets, we attached an event handler to change the value of the open variable to show the modal.
Update Blog
To update the blog post, we'll create a Sveltekit dynamic route. This route will use the id of each blog as a param. Sveltekit implements file-system-based routing, which means that your application routes are defined by your directories, and version 3 requires you to have a +page.svelte and a +page.js or +page.server file in each of the directories.
You can learn more about the Sveltekit routing here. Now create a post/[id] folder in the routes for the post route. In the [id] folder, create an +page.svelte and +page.ts files and add the code snippet below in the +page.ts file.
/** @type {import('./$types').PageLoad} */
export async function load({ params }) {
const { id } = params
const data = await fetch(`https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev/posts/${id}`).then(res => res.json());
return data
}
In the above code snippet, we have a load function that will load data from the API, and the function takes the params as an object, which gives us access to the params objects to access the post id in the URL.
Then we send a request to the API to get a blog post whose Id is in the requested parameter. This will apply to all the blog posts we click. The load function will return a serializable JSON value which we can access in the +page.svelte page through the data object.
Now add the code snippet below to the +page.svelte page.
<script>
import Button from '@smui/button';
/** @type {import('./$types').PageData} */
export let data;
import Textfield from '@smui/textfield';
import HelperText from '@smui/textfield/helper-text';
import Card, { Content } from '@smui/card';
import CharacterCounter from '@smui/textfield/character-counter';
import { goto } from '$app/navigation';
let valueA = data.title;
let value = data.content;
async function editPost() {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev/posts/${data.id}`, {
method: 'PATCH',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
title: valueA,
content: value
})
}).then((res) => {
res.json();
goto('/');
});
}
</script>
<div class="card-display">
<div class="card-container">
<Card padded>
<Textfield variant="outlined" bind:value={valueA} label="Edit Title">
<HelperText slot="Edit Title">Helper Text</HelperText>
</Textfield>
<br />
<Textfield textarea input$maxlength={2500} bind:value label="Edit Content">
<CharacterCounter slot="internalCounter">0 / 100</CharacterCounter>
</Textfield>
<br />
<Button on:click={editPost}>Edit</Button>
</Card>
</div>
</div>
In the above code snippet, we imported the components to create a UI for this page with the Card, Textfield, and Button components. In each of these components, we displayed the details post data in their values so the user can only edit the part they want.
Then we created an editPost function which sends a Put request to the API with the data we which to update in the payload as JSON.

Delete Blog
We also need to allow the users to delete posts. We have attached a delete button to the posts in the data table in the components/Table.svelte file. So add the code snippet below in the script tag to delete a post from the API.
async function deletePost(id: number) {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev/posts/${id}`, {
method: 'DELETE'
}).then((res) => {
res.json();
location.reload();
});
}
Then update the delete button to attach the function to an on:click event.
<Button on:click={() => deletePost(item.id)}>Delete</Button>
Conclusion
Throughout this tutorial, we've implemented how to create a CRUD application using Sveltekit. We started by knowing what Sveltekit is all about. Then we built a blog application for the demonstration. Now that you have the knowledge you seek, how would you use Sveltekit in your next project? Perhaps you can learn more about Sveltekit from the documentation.
Live StackBlitz Example
Build your React-based CRUD applications without constraints
Modern CRUD applications are required to consume data from many different sources from custom API’s to backend services like Supabase, Hasura, Airtable and Strapi.
Check out refine, if you are interested in a backend agnostic, headless framework which can connect 15+ data sources thanks to built-in providers and community plugins.
refine is an open-source React-based framework for building CRUD applications without constraints. It can speed up your development time up to 3X without compromising freedom on styling, customization and project workflow.
refine is headless by design and it connects 30+ backend services out-of-the-box including custom REST and GraphQL API’s.
Visit refine GitHub repository for more information, demos, tutorials, and example projects.




